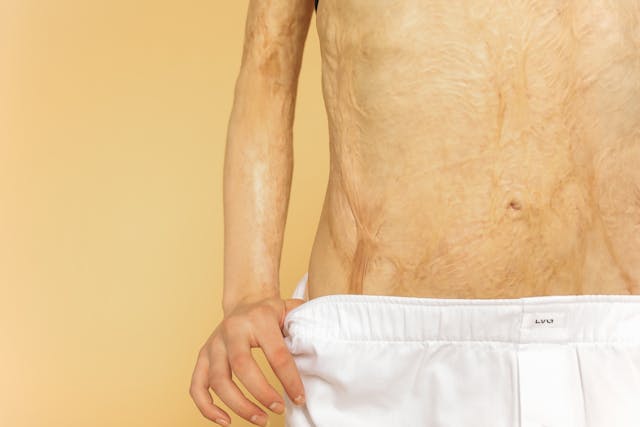
Burns are one of the most painful and complex types of injuries a person can experience. They range from mild discomfort to severe impairment, permanently affecting the body’s mobility and overall quality of life. While immediate medical care focuses on treating burns, the long-term challenges of rehabilitation are often just as significant.
Type of burn and its severity
Burns are divided into three broad categories based on the depth and severity of the injury.
- first degree burn is the mildest, affecting only the outermost layer of skin, causing redness and pain. These burns usually heal within a few days to a week and have minimal long-term effects.
- second degree burns Penetrates deep into the skin, reaching the second layer (the dermis) and causes blisters, severe pain, and swelling. Although second-degree burns can cause scarring, they are usually treatable with proper care.
- third degree burns Destroying the epidermis and dermis may reach deeper tissues such as muscles, tendons, and even bones. These burns are serious and often require surgical intervention, such as skin grafting.
The more severe the burn, the greater the potential impact on mobility and overall body function. Burns that occur on or near joints (such as knees, elbows, or hands) can severely limit movement, and severe burns can lead to long-term complications and make even simple daily tasks difficult.
Physical impact on daily life
The physical consequences of burn injuries can be overwhelming. Burns affect not only the skin, but also the muscles, nerves, and bones beneath the surface. This section discusses the main ways burns affect physical health and mobility.
pain and sensitivity
Even after the initial burn has healed, the pain can linger for months or even years. The burned area may become allergic to touch, temperature, and pressure. Victims often report discomfort caused by clothing rubbing against scar tissue or exposure to heat or cold. High levels of sensitivity can make everyday activities like getting dressed or cooking a meal painful.
reduced range of motion
One of the most important physical limitations that burn survivors face is reduced range of motion. Burn scars can shrink, tightening the skin and limiting movement, especially if the burn is close to a joint. For example, burns to your arms or legs can make it difficult to bend your elbows, knees, or ankles, seriously affecting your ability to move. In some cases, people may need physical therapy to prevent permanent stiffness and regain as much mobility as possible.
Loss of strength and muscle control
In severe burns where muscle tissue is damaged, victims may lose muscle strength or control. This loss can make even the simplest tasks, such as walking or holding objects, extremely difficult. Burn survivors may need extensive rehabilitation to regain muscle strength and control, and some may never fully regain their pre-injury abilities.
Rehabilitation and physical therapy needs
Recovery is often a long-term commitment for burn survivors. Physical therapy is essential to improve mobility and prevent permanent loss of function. Treatment focuses on stretching the skin and scar tissue to maintain flexibility, strengthening weak muscles, and improving coordination and balance. Without rehabilitation, burn survivors face a higher risk of long-term disability due to immobility.
Emotional and psychological effects
The physical consequences of burn injuries are only one aspect of the recovery process. Burn survivors often face emotional and psychological challenges that may impact their ability to participate in daily life.
body image issues
Burns, especially severe burns, can leave lasting scars that can significantly change a person’s appearance. These noticeable changes may lead to body image issues, causing the individual to feel self-conscious or anxious in social situations. Some people may avoid social interaction altogether, leading to feelings of isolation.
anxiety and depression
Burn survivors are at higher risk for mental health problems such as anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The trauma of a burn incident, coupled with ongoing pain and restrictions, can be overwhelming. Mental health support is vital to helping individuals cope with these emotional challenges.
Impact on social life
The combination of physical limitations and emotional challenges can impact a person’s social life. Burn survivors may withdraw from activities they once enjoyed because of appearance embarrassment or the inability to participate fully. This isolation can further impact their mental health and recovery process.
Impact on daily tasks
Burns can make once-simple daily activities, such as bathing, getting dressed, or preparing meals, extremely difficult.
Severe burns can limit a person’s ability to perform daily activities. For example, burns on your hands may make it difficult to button your shirt, while burns on your legs may cause pain when walking or standing for long periods of time. Simple tasks such as washing dishes or folding laundry can become overwhelming and assistance may be needed.
In cases where burn injuries severely limit mobility, an individual may need to rely on assistive devices such as crutches, wheelchairs or walkers to get around, said an attorney who specializes in burn injuries. Others may need a full-time caregiver to help with daily tasks, which may affect their independence and self-esteem.
long term recovery and recovery
Recovering from a burn injury is a long and difficult journey that often requires physical and emotional support. Recovery is a critical part of the recovery process.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in helping burn survivors regain mobility. Therapists work with patients to stretch scar tissue, improve flexibility, and strengthen muscles to increase range of motion. Without treatment, survivors are at risk of permanent stiffness, which will further limit mobility.
Occupational therapy helps burn survivors adapt to new restrictions and learn new ways to perform daily tasks. This type of treatment focuses on improving fine motor skills, such as grasping and holding objects, as well as strategies to regain independence in personal care and household chores.
Skin grafts and surgery
For severe burns, skin grafts and other surgeries may be needed to improve mobility. These surgeries are designed to reduce scar tissue that limits movement and restore the appearance and function of the damaged area.
While recovery is crucial, prevention is equally important. Avoiding burns in the first place is the best way to prevent the long-term complications discussed in this article. Safety tips include using caution around open flames, handling chemicals with care, and using protective gear in hazardous environments.
Burn injuries can significantly impact a person’s daily life and mobility, but with appropriate medical care, recovery, and emotional support, many survivors are able to rebuild their lives. Understanding the full range of challenges burn victims face, from physical limitations to emotional recovery, can help provide the necessary support and resources for recovery.